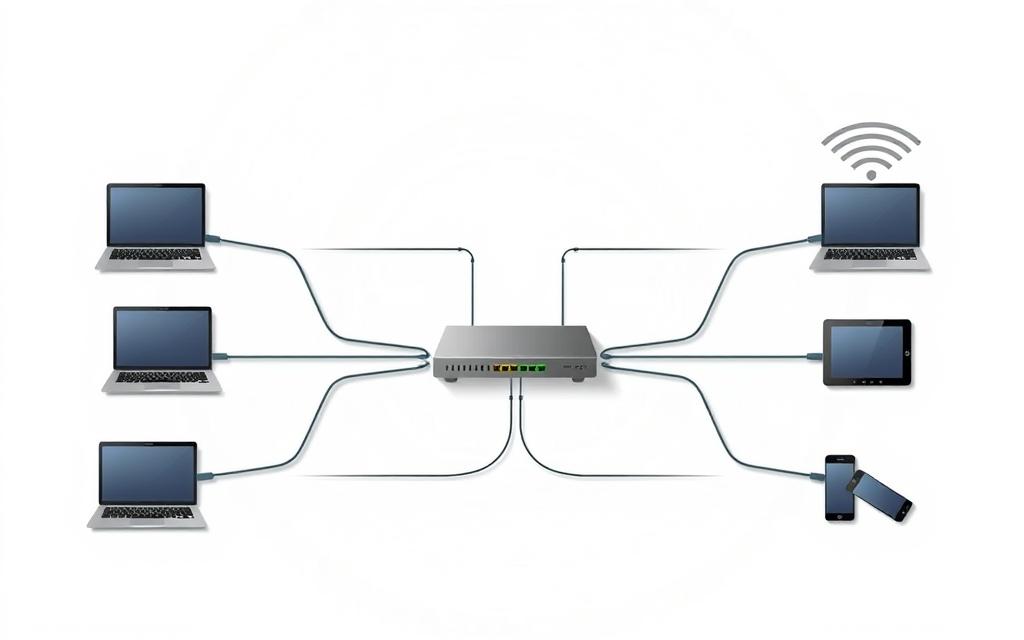
Imagine many devices working together, sharing info and resources over long distances. This is what modern digital connectivity is all about.
These systems use special rules to send data fast and well. They help us send emails and use cloud services.
The history of these systems goes back to the late 1950s. Today, they are much more advanced. Knowing how they work helps us understand our digital world.
This basic knowledge is key for both personal chats and big business operations. It makes it easy to connect and share across different devices and platforms.
What is a Computer Network: Simple Definition
A computer network is a digital space where devices work together. It connects different computing tools into one unit. This unit can share information and use each other’s strengths.
The Basic Idea: Connecting Computers and Devices
A network connects many connected devices through set rules. Each device, or node, can send, receive, or pass on data. This makes the digital world more connected.
These nodes include computers, servers, printers, smartphones, and even wireless earbuds. When they work together, they become much more powerful than alone.
Primary Goal: Sharing Resources Efficiently
Networks aim to share resources well among devices. This sharing boosts work efficiency in many ways.
Computing power, storage, and data become available to all users. Printers, once for one person, now serve everyone. This makes things more efficient and cost-effective.
Real-World Examples: Home and Office Networks
Home networks link devices for internet, streaming, and sharing files. They make home entertainment and work easier for families.
Office networks help teams work together by sharing printers, servers, and data. This way, everyone can work on projects together, keeping everything up to date and secure.
Both home and office networks show how networks make things better together. They use resources wisely, making the whole more than the parts.
Essential Components of a Computer Network
To build a working computer network, you need three key parts. These parts work together to create a digital connection system. This system can be small, like a home network, or big, like a company’s network.
Hardware: Devices like PCs, Routers, and Switches
Network hardware are the physical tools that let systems talk to each other. Devices like computers, laptops, and phones are used every day.
Networking equipment is the middle layer. Routers help move data between networks. Switches connect devices in the same network. Modems, wireless access points, and bridges also play important roles.
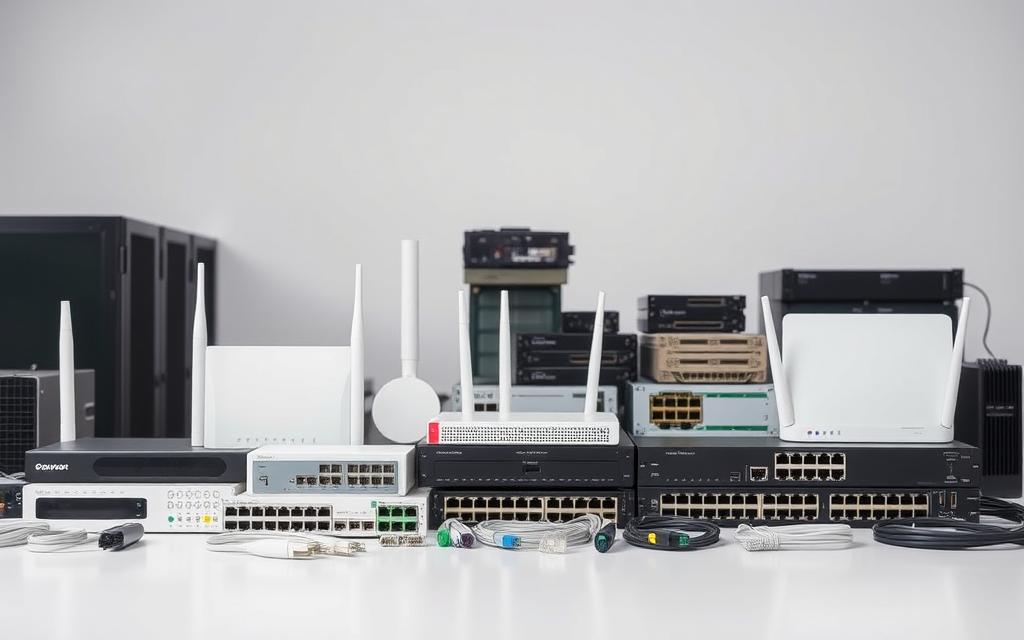

Each network hardware has its own job in managing data. Knowing about these devices helps in creating efficient networks for different types of networks.
Connection Media: Ethernet Cables and Wi-Fi
Transmission media is how data moves between devices. Wired connections use Ethernet cables or fibre optics for fast data transfer.
Wireless tech has changed how we connect. Wi-Fi lets devices move freely without cables. Bluetooth and infrared are for short-range and line-of-sight data transfer.
Choosing between wired and wireless depends on speed, security, and the environment.
Software: Protocols such as TCP/IP
Networking software controls how devices talk to each other. Protocols set the rules for data exchange.
The TCP/IP suite is key for internet communication. It includes HTTP for web, FTP for files, SMTP for email, and DNS for domains.
These protocols help devices and apps work together, even if they’re different. For more info, check out the basic computer network components page.
Setting up networking software right is key for security, speed, and reliability in all networks.
Different Types of Computer Networks
Computer networks vary in size and purpose. Knowing about these types helps organisations choose the right network for their needs.
Local Area Network (LAN): For Small Areas
A Local Area Network connects devices in a small area. Offices, schools, and homes use LANs.
LANs allow fast data transfer between devices. They are common for everyday computing.
Wide Area Network (WAN): For Large Distances
Wide Area Networks span large areas, linking many LANs. Companies use WANs to connect offices across cities or countries.
The internet is the biggest WAN. It uses technologies like leased lines and satellites.
Other Networks: PAN, MAN, and VPN
Personal Area Networks connect devices around a person. Bluetooth links between phones and headphones are examples.
Metropolitan Area Networks cover areas bigger than LANs but smaller than WANs. They are used in city-wide networks.
Virtual Private Networks create secure paths over public networks. Remote workers use VPNs to safely access company resources.
New types include Software-Defined WAN and cloud networks. They offer flexibility and scalability for today’s businesses.
How Data Travels in a Network
Information moves between devices in a complex way. This shows the amazing mechanics of modern connectivity. It uses systems that make sure data is sent efficiently and reliably across all networks.
Data Packets: The Building Blocks of Transmission
When you send data, it breaks down into smaller units called packets. Each packet has a part of the data and important header info.
The header has details like where the data comes from and where it’s going. This way, if a packet gets lost, only that one needs to be sent again. This makes the whole process more efficient.
This method is key to how we send data today. It lets networks handle lots of messages at once without losing efficiency.

IP Addresses: Identifying Devices on the Network
Every device on a network needs a unique digital address. This is called an IP address. It helps find and talk to devices on the network.
IP addresses look like numbers separated by dots, like 192.168.1.1. They help identify devices and where they are on the network.
There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses. This system is the base of all network communication.
Key Protocols: TCP/IP and HTTP Explained
Network protocols are like rules for devices to talk to each other. They make sure different systems can understand each other. The TCP/IP suite is the most important set of these protocols.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that makes sure data is delivered right. It sets up connections and packs data into packets. IP handles the addresses and routes packets to their destinations.
HTTP is for web communications. It tells how messages are formatted and sent between web servers and clients. It helps load web pages and send web content.
These network protocols work together to make data transmission possible. Knowing how they work helps us understand the internet better. They make sure we can communicate reliably across the world.
Advantages of Using Computer Networks
Computer networks bring many benefits that change how we work and live. They make information flow smoothly and help us work better together. This is a big step forward in how we use computers today.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Computer networks change how we talk and work together. Instant messaging lets us chat in real time, no matter where we are. Video calls make meetings easy, without the need to travel.
Emails help us send messages with files and keep things organised. Tools for working together on documents make projects faster and teams stronger. This all helps us get things done quicker and work better together.
Cost Savings through Shared Resources
Using computer networks saves a lot of money. Instead of buying many devices, we can share resources. This means fewer printers and less money spent on them.
Having one scanner and storage for everyone saves on equipment costs. Buying software for servers instead of computers also cuts costs. This makes IT easier to manage and saves energy too.
| Resource Type | Individual Setup Cost | Network Shared Cost | Savings Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Quality Printer | $800 per unit | $1,200 shared | 70% with 10 users |
| Document Scanner | $400 per unit | $600 shared | 75% with 8 users |
| Storage Server | $300 per computer | $2,000 centralised | 60% with 15 users |
| Software Licenses | $150 per seat | $800 site license | 65% with 12 users |
Centralised Data Storage and Enhanced Security
Networks make managing data better. All important files are kept in one place, making backups easy. This means we never lose important files because of a broken device.
Having all security in one place makes it stronger. Admins can control who sees what, and firewalls keep data safe. This makes sure our data is always secure.
Keeping the network up to date is easy. This stops problems and keeps everyone safe. It’s a safe place to work, making our jobs easier.
These benefits make computer networks essential today. They save money, make us work better, and keep our data safe. It’s a smart choice for our digital world.
Everyday Applications of Computer Networks
From morning coffee to evening entertainment, computer networks power our daily lives. They have grown from special tools to key parts of our modern world. They support us in many areas.

Home Uses: Internet Browsing and Streaming
Home networks make many daily activities possible. They let families access the internet and enjoy streaming services. This brings entertainment right to our living rooms.
Today’s homes use networks for:
- Watching movies and music on Netflix and Spotify
- Playing games online with others
- Controlling smart home devices
- Sharing files between devices
- Video calls with loved ones
These uses have changed how we relax, talk, and manage our homes. Being able to watch content from anywhere is just one benefit of good home networks.
Business Applications: Emails and File Sharing
Businesses need strong networks to work well and stay competitive. Emails are key for fast communication between teams and worldwide.
Companies use networks for:
- Working together on documents with SharePoint
- Managing customer relationships
- Tracking inventory and supply chains
- Using cloud apps
- Sharing and storing files securely
These networks help businesses run smoothly and save money by sharing resources. Good network solutions can really help a company succeed.
Networks in Education and Public Services
Schools and public services use networks to improve their work. They use digital tools for learning, research, and managing schools.
Important uses include:
- Online learning systems
- Digital libraries and research databases
- Tools for working together
- Systems for student info
Public services use networks for health records, emergency planning, and government services. These networks help make sure services reach people well and on time.
Using networks in education and public services has made a big difference. These systems are now key parts of our society.
Conclusion
This summary shows how networks connect us all. They are key to our daily lives, from browsing the internet to running businesses.
Devices talk to each other through hardware, software, and protocols. These systems have grown from simple links to complex networks. They support global business and personal chats.
New tech like cloud computing, IoT, and 5G is changing networks. Knowing about these changes is vital in our connected world.
Being computer literate now means understanding networks too. It helps us see how data moves between devices. This knowledge is useful at home and at work.
The future will see even more advanced networks. Keeping up with tech news helps us adapt to digital changes in our lives.
FAQ
What is a computer network in simple terms?
A computer network is a group of devices like computers and printers. They can share data and resources. This happens over wired or wireless connections.
What are the main goals of a computer network?
The main goals are to share resources and enable communication. This makes it easier for devices and users to work together.
What hardware is essential for building a computer network?
You need devices like PCs and smartphones. Also, networking gear like routers and switches. And cables and wireless access points for connections.
What are the different types of computer networks?
There are many types. LANs for small areas, WANs for big areas, and special ones like PANs and VPNs.
How does data travel across a network?
Data is split into packets with details on where they’re going. These packets follow paths set by protocols like TCP/IP. Devices are identified by unique IP addresses.
What are the key benefits of using computer networks?
Networks improve communication and save costs. They help manage data and offer security with firewalls and encryption.
How are computer networks used in everyday life?
Networks are used for internet browsing and streaming. They support online gaming and smart home systems. They also help with business and public services like healthcare.
What role do protocols like TCP/IP play in networking?
Protocols like TCP/IP manage data transmission. TCP ensures reliable communication, while IP handles addressing and routing.
Can you explain what a LAN and WAN are?
LANs cover small areas like a building. WANs connect larger areas, like cities or countries. The internet is a big WAN example.
How do computer networks enhance security?
Networks make it easier to apply security measures. This includes firewalls and encryption to protect against threats.
What is the significance of IP addresses in networking?
IP addresses are unique identifiers for devices. They help route data accurately, like a postal address.
How have computer networks evolved over time?
Networks have grown from simple connections to complex systems. They now support global communication and IoT. They keep adapting to new technologies like 5G.