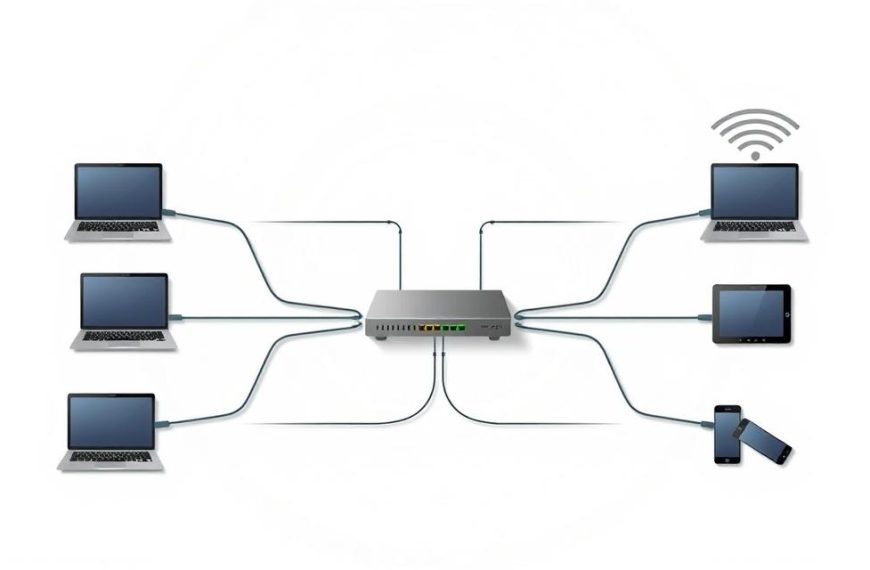
Think of your network as a secure building with one guarded entrance. This entrance connects your internal systems to the wider world of networks. It’s called a network gateway.
This key node acts as your network’s main entrance. It translates data so it can travel between different networks. Without it, systems can’t talk to each other.
As Cisco explains, these devices also have security features. They check all traffic coming in and out, keeping your network safe.
The default gateway is your network’s exit to other networks. It’s where data goes first when it leaves your network. It’s a vital part of today’s digital world.
Understanding Network Gateways: The Essential Bridge
Network gateways are key in today’s digital world. They act as smart translators between different networks. Unlike routers, gateways have unique roles that are vital for smooth communication across various networks.
Core Definition and Purpose
A network gateway is a protocol converter. It lets different networks talk to each other, even if they use different ways to send data. Unlike simple devices, gateways can change data packets as they move between networks.
The main job of a gateway is to connect different networks. This includes linking local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs) or the internet. Gateways make sure data moves well between these networks.
These devices work at the network layer of the OSI model. But they can work on any layer, depending on their setup. This means gateways can handle many types of network traffic and standards.
How Gateways Differ from Routers
The main difference between router vs gateway is their job and what they can do. Both help with network communication, but in different ways.
Routers mainly work within a network. They use IP addresses to send data packets. This helps data move efficiently within similar networks.
Gateways, on the other hand, connect different networks. They do protocol conversions that routers can’t. This is key when networks with different standards need to talk to each other.
Before, gateways and routers were separate devices. Now, they’re often in one device called a router. But the gateway part is very important in these combined units.
As networking tech has grown, the difference between gateways and routers has gotten smaller. But knowing their roles is key for designing and setting up networks. This is very important for complex networks or special communication protocols.
What is a Gateway in Computer Network: Key Functions
Network gateways act as smart middlemen. They help different systems talk to each other smoothly. They do this by changing data from one format to another.

Protocol Conversion Capabilities
Gateways are great at changing network protocols. They act like digital translators. This lets devices with different ways of talking share information.
Imagine a smart home with Bluetooth sensors and a TCP/IP network. The gateway makes sure data moves smoothly between them.
Gateways do more than just translate. They handle:
- Packet structure transformation
- Address resolution between protocols
- Error handling methodology conversion
- Session management across different standards
Data Format Translation
Gateways are also experts in changing data formats. They make information fit for use on different platforms and systems.
For example, old analogue phones can connect to VoIP networks through gateways. They turn voice signals into digital packets, keeping quality high.
In cloud storage, gateways help apps work with cloud services. They change API calls into block-based storage protocols. This lets apps use cloud storage without changing their code.
The translation process includes:
- Media conversion (analogue to digital)
- Data encapsulation format changes
- Compression algorithm adaptation
- Encryption method transformation
Gateways are key for modern networks. They bridge technology gaps while keeping data safe and running smoothly.
Types of Network Gateways
Network gateways are designed for different needs. They help organisations pick the best for their networks.
Residential vs Enterprise Gateways
Home networks use residential gateways. They offer simple, all-in-one solutions. These devices make internet access easy for daily use.
Businesses need enterprise gateways for their networks. They handle more traffic and offer better security. These devices support complex networks and critical apps.
Specialised Gateway Types
There are gateways for specific needs. They fill gaps in modern networks.
Voice Gateways for Telecommunications
A VoIP gateway changes phone signals into digital data. This lets voice calls work over the internet. It supports both old and new phone systems.
Voice gateways help businesses save money on calls. They link old phone systems with new VoIP ones. This is key in the shift to modern communication.
Cloud Gateways for Modern Infrastructure
Cloud storage gateways connect local networks to the cloud. They make moving data between systems easy. This supports hybrid cloud setups.
These gateways also improve data transfer. They ensure data is safe when moving between networks and the cloud. They help with managing data in today’s world.
Other gateways include IoT and wireless ones. IoT gateways link smart devices to IT systems. Wireless gateways offer mobile internet access.
| Gateway Type | Primary Function | Typical Environment | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Gateway | Basic internet access | Home networks | All-in-one design, user-friendly |
| Enterprise Gateway | High-performance networking | Business organisations | Advanced security, traffic management |
| VoIP Gateway | Voice communication conversion | Telecommunications | Analogue/digital translation, protocol support |
| Cloud Storage Gateway | Cloud integration | Hybrid infrastructure | API translation, data caching |
| IoT Gateway | Device connectivity | Smart environments | Protocol conversion, sensor integration |
| Wireless Gateway | Mobile connectivity | Various environments | Combined functionality, flexibility |
Gateway Implementation in Network Architecture
Adding a gateway to your network needs careful thought. You must decide between physical devices and software. This choice affects how well your network works, how it grows, and how easy it is to manage.

Hardware vs Software Gateways
Network managers often pick between hardware gateway devices and software gateway options. Hardware gateways are special devices with built-in software for network tasks.
These devices are made for top performance and have extra security features. Many modern routers now have gateway functions, making them great for small businesses.
On the other hand, software gateways run on regular servers or virtual machines. This lets companies use what they already have and grow their gateway functions as needed. This is why software gateway solutions are getting more popular in fast-changing business settings.
| Implementation Type | Best Use Cases | Performance Impact | Scalability Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Gateway | High-throughput networks, dedicated security zones | Optimised for specific functions | Limited to device capacity |
| Software Gateway | Virtualised environments, cloud deployments | Depends on host system resources | Easily scalable through replication |
| Router-Integrated | Small to medium businesses, branch offices | Balanced performance for multiple functions | Limited to router capabilities |
Configuration Best Practices
Setting up a gateway right is key for a stable and fast network. Using DHCP makes it easier to set up IP addresses in big networks. This cuts down on mistakes and makes managing the network simpler.
But, sometimes you need to set things up manually for certain tasks. It’s important to keep track of these settings and have backups. Checking your setup regularly helps keep everything running smoothly.
Here are some key things to remember:
- Have backup gateways for important network paths
- Keep your gateway’s software and firmware up to date
- Always watch how your gateway is doing
- Test how your gateways switch over during maintenance
Whether you choose a hardware gateway or a software solution depends on your network needs, budget, and skills. Both can work well if set up and looked after properly.
Security Considerations for Network Gateways
Network gateways are key security points. They control all network traffic coming in and out. They are vital for keeping networks safe from threats.
Gateway Security Features
Modern gateways have many security layers. Firewalls are the first defence, filtering traffic based on rules. They check data packets and block suspicious activity.
Proxy servers add extra protection. They sit between users and the internet, filtering content and controlling access. They block harmful websites and prevent unauthorised access.
Secure Internet Gateways (SIGs) are cloud-based solutions. They offer threat protection, data loss prevention, and application control. They ensure consistent security across networks.
Enterprise gateways also have:
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems
- Virtual private network (VPN) capabilities
- Antivirus and anti-malware scanning
- Content filtering and application control
- Traffic monitoring and logging systems
| Security Feature | Primary Function | Implementation Level | Common Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firewall | Traffic filtering and access control | Essential for all networks | Cisco ASA, pfSense, FortiGate |
| Proxy Server | Content filtering and anonymity | Common in enterprise environments | Squid, Microsoft Forefront TMG |
| Secure Internet Gateway | Comprehensive cloud security | Growing adoption in distributed networks | Zscaler, Cisco Umbrella |
| Intrusion Prevention | Threat detection and blocking | Advanced security requirement | Snort, Suricata, commercial IPS |
Common Gateway Vulnerabilities
Gateways can be weak if not kept up. Default settings are often risky, with easy-to-guess passwords. Hackers use these to get into systems.
Old software is another big risk. Updates fix security holes, but many wait too long. This leaves networks open to attacks.
Bad security rules can also be a problem. If rules are too open, bad traffic can get through. Regular checks help fix these issues.
Denial-of-service attacks aim to shut down gateways. They flood the gateway with traffic, disrupting services. Using rate limits helps fight these attacks.
Keeping gateways secure needs ongoing effort. Regular checks, updates, and the right setup are key to protecting networks.
Gateway Performance and Optimisation
Keeping your gateway in top shape is key. It’s where networks meet, handling a lot of traffic. This can slow things down. By watching performance closely and fixing problems early, your network stays fast and reliable.
Performance Monitoring Techniques
Watching your gateway helps you understand your network better. It’s a key spot for checking how things are running.
Good monitoring includes:
- Checking for delays in connections
- Watching how much bandwidth is used
- Finding out if there are any errors in sending data
- Seeing how often connections are successful
Many use special tools to keep an eye on things. These tools show important stats in real-time. They can also warn you of problems before they cause trouble.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When problems pop up, the gateway is often the first place to look. A clear plan for fixing issues helps solve problems fast.
First, try pinging the gateway to see if it’s working. If it’s not, check a few things:
- Make sure the physical connections and power are okay
- Check the IP settings and subnet
- Look at firewall rules to see if they’re blocking needed traffic
- See if the firmware needs an update
If problems keep coming back, use more detailed tools. They can show more about what’s going on and help find mistakes in settings.
| Common Gateway Issue | Primary Symptoms | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Unresponsive Gateway | Complete network outage, failed pings | Check power, reboot device, verify physical connections |
| Incorrect Subnet Configuration | Devices cannot communicate across networks | Verify subnet masks, update routing tables |
| Bandwidth Saturation | Slow network performance, timeouts | Implement traffic shaping, upgrade capacity |
| Security Rule Conflicts | Specific services unavailable | Review firewall settings, adjust access rules |
By keeping an eye on things and fixing problems early, your gateway stays reliable. For more on gateways, check out our guide on the role of gateways in computer networks.
By following these steps, your gateway will keep your network running smoothly. It won’t slow you down.
The Evolution of Network Gateways
Network gateways have changed a lot over time. They’ve moved from being just hardware to being advanced solutions. This change shows how digital networks have grown over the years.
Knowing how gateways have changed helps us understand their current and future roles. Their job has grown beyond just changing protocols.
From Early Networking to Modern Implementations
In the early days of computers, gateways and routers were different devices. Gateways changed protocols between networks. Routers moved packets within the same network.
In the 1990s, things started to get more integrated. As tech improved, devices combined functions to save money and make networks easier to manage. This trend got stronger in the 2000s.
Now, devices do many things at once. They handle routing, firewalls, VPNs, and more in one unit. The Asterfusion ET2500 egress gateway is a good example of this.
| Era | Gateway Characteristics | Primary Functions | Typical Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980s-1990s | Dedicated hardware devices | Protocol conversion, basic translation | Enterprise networks only |
| 2000s-2010s | Integrated router-gateway combos | Multi-protocol support, basic security | Business and residential use |
| 2020s-Present | All-in-one intelligent solutions | Full network stack consolidation | Universal across network types |
Future Trends in Gateway Technology
Future gateways will be smarter and more connected to the cloud. New future trends will use software-defined networking. This makes managing networks easier from one place.
Gateways will be key for IoT systems. They’ll help devices talk to each other and to the internet. They’ll also keep data safe.

Next-generation gateways will also be important for multicloud setups. They’ll help connect different cloud services and local networks. This is good for companies that use both cloud and local systems.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be at the forefront of gateway future trends. These technologies will help networks work better and stay safe. Gateways will make smart choices to improve performance and security.
The journey of network gateways from simple translators to smart network managers is ongoing. This evolution keeps gateways important in today’s complex digital world.
Conclusion
A network gateway is key for computer network communications. It lets different networks talk to each other by changing protocols and translating data.
Gateways are vital for network bridging. They help various systems work together. They also keep networks safe and connect them smoothly.
Gateways are important in many areas, from home internet to big business networks. They are the base of today’s digital world. Cloud services also depend on them to manage traffic and keep things running smoothly.
Gateway technology keeps getting better. As networks get more complex, gateways adapt. They handle more security, speed, and work with different systems.
It’s important for network experts and companies to know how gateways work. They will keep improving to tackle new challenges and opportunities in networking.
FAQ
What is a gateway in a computer network?
A gateway is a key part of a network. It lets data in and out, connecting different networks. It changes protocols so different networks can talk to each other, like a LAN to the internet.
How does a gateway differ from a router?
A gateway works at higher levels of the OSI model, focusing on protocol changes. Routers, at Layer 3, mainly move data within the same network. Today, many devices do both jobs.
What are the key functions of a network gateway?
The main jobs are converting protocols and formats. For example, it might turn Bluetooth into TCP/IP. It also changes data formats, like analogue signals to digital VoIP packets.
What types of gateways are commonly used?
There are many types. Home gateways are all-in-one for homes. Business gateways are for complex networks. There are also gateways for VoIP, cloud, and IoT.
How are gateways implemented in a network?
Gateways can be hardware or software. They can be set up dynamically or manually for better control.
What security features should a gateway have?
It should have firewalls, proxy servers, and Secure Internet Gateways. These protect against threats. It’s important to keep gateways secure as they are the main entry point.
How can gateway performance be monitored and optimised?
Performance can be checked by looking at traffic and health. Troubleshooting includes checking connections and using tools like ping.
How have gateways evolved over time?
Gateways have changed from single-purpose devices to all-in-one units. They now handle routing, security, and analytics. This supports new technologies like IoT and multicloud.